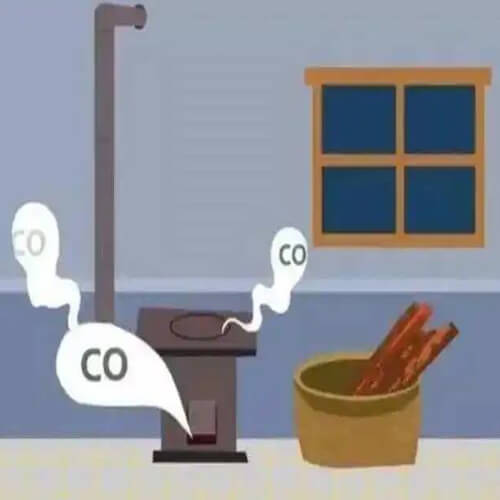
Carbon monoxide is a colorless and odorless toxic gas at room temperature. People cannot perceive its presence through smell. Therefore, carbon monoxide is often referred to as the “silent killer.” In production and daily life, incomplete combustion of carbon-containing substances can produce carbon monoxide, which can lead to poisoning when inhaled by humans. Carbon monoxide is not harmful in well-ventilated environments, but it becomes dangerous in enclosed spaces such as basements, kitchens, garages, or campers.
Although carbon monoxide gas is toxic, it plays an important role as a combustible and clean energy source in the industrial and metallurgical sectors. It can participate in redox reactions to purify metals. Carbon monoxide gas is highly flammable and explosive. To prevent accidents, we need to use carbon monoxide detector. These detectors can continuously monitor the concentration of CO gas in the environment and emit an alarm signal when it reaches the set alarm threshold, reminding us to take preventive measures.
About Carbon Monoxide
Where does carbon monoxide come from?
- Vehicle exhaust is a major source of carbon monoxide in cities. Especially during heavy traffic congestion, when vehicles are idling, the high concentration of gasoline leads to incomplete combustion, resulting in the emission of a large amount of carbon monoxide. However, when vehicles are traveling at high speeds, the emission of carbon monoxide is relatively low.
- Incomplete combustion of carbon-containing materials or fossil fuels in industrial production can generate varying levels of carbon monoxide. Examples include steelmaking, iron smelting, coking, oil refining, gas processing, and exhaust gases from internal combustion engines.
- Carbon monoxide emissions in the process of mining are associated with underground fires, slow oxidation of coal, blasting operations, and explosions of gas and coal dust. Therefore, underground operations are usually equipped with detectors that have carbon monoxide detection and warning functions to ensure the safety of the personnel involved.
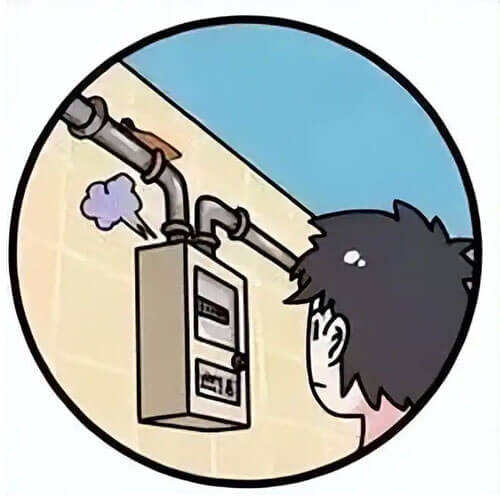
- Carbon monoxide emissions are also associated with household stoves, gas plants, and the use of domestic gas and stoves.
What is the danger of carbon monoxide?
Carbon monoxide has a strong affinity for hemoglobin in the blood, which can cause a rapid decrease in oxygenated hemoglobin in the plasma, thereby preventing the transportation of oxygen in the blood. Mild carbon monoxide poisoning can manifest as symptoms such as headache, dizziness, and feeling of pressure in the head. Moderate or severe carbon monoxide poisoning may result in initially increased and then decreased blood pressure, irregular heart rate, and in severe cases, loss of consciousness or even death.
How can I prevent carbon monoxide poisoning?
- Using gas stoves, fireplaces or gas water heaters in a closed environment carries the risk of carbon monoxide gas accumulation. When using, open the windows to ensure indoor air circulation, which can effectively reduce the risk of carbon monoxide poisoning.
- Regularly maintain gas pipelines to prevent gas leaks. If using a gas water heater, regularly inspect the lines and valves to ensure that the appliance is not malfunctioning.
- Properly install showers and avoid installing water heaters in bathrooms. Regularly clean and check the flaps of range hoods to ensure they can automatically open and prevent exhaust gases from flowing back.
- If accidentally exposed to a high concentration of carbon monoxide, turn off the gas source, open doors and windows, and wear a protective mask or cover your mouth and nose with a damp cloth.
- Do not run a vehicle in the garage. If you want to warm up your car in winter, first drive it out of the garage. Carbon monoxide is a common byproduct of vehicle exhaust and can quickly accumulate in an enclosed garage.
- Install carbon monoxide detectors at important locations to monitor carbon monoxide gas concentration in real time to avoid danger.
About Carbon Monoxide Detector
What is carbon monoxide detector?
A carbon monoxide detector, also known as a CO detector, senses the concentration of carbon monoxide gas in the air through an internal carbon monoxide sensor and converts it into an electrical signal output. The magnitude of the electrical signal is related to the concentration of carbon monoxide.
How does a carbon monoxide sensor work?
Currently, carbon monoxide sensors for detection can be categorized into semiconductor, electrochemical, infrared, and catalytic combustion types, based on their detection principles. Here is an analysis of their main working principles and advantages/disadvantages:
Semiconductor sensors
Pros: High sensitivity. Trace gas concentrations can be measured.
Small size and low cost.
Cons: Susceptible to interference from other gases, which may affect its detection accuracy.
Greatly affected by temperature.
Semiconductor gas sensors use changes in semiconductor resistance to detect gas composition or concentration. According to different physical properties, semiconductor gas sensors can be divided into resistive and non-resistive types. The resistive semiconductor gas sensor uses the change in resistance caused by the semiconductor to contact the gas to detect the concentration of the gas. The non-resistive semiconductor gas sensor directly detects the gas based on the adsorption and reaction of the gas, causing certain characteristics of the semiconductor to change. or indirect detection.
The sensitivity of the semiconductor gas sensor is very high. It is like a vigilant “watchman”, extremely sensitive to the presence of specific gases, and can even detect trace gas concentrations. Such keen sensitivity not only facilitates industrial production, but also shines in fields such as environmental protection and medical diagnosis. However, the sensitivity of semiconductor gas sensors is affected by temperature. In high or low temperature environments, sensitivity will be affected, resulting in slower reaction speed or unstable detection results. This is like a person’s reaction becoming slower in a cold or hot environment.
The principle of an electrochemical sensor is illustrated in the diagram below.
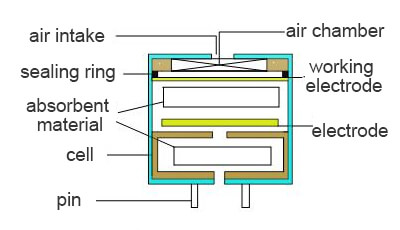
Pros: Small size, low power consumption, high sensitivity, good stability, good linearity, good repeatability, and longer lifespan.
Cons: There are significant differences in price, performance, and manufacturing processes among different brands of electrochemical sensors.
When a fixed voltage is applied to the positive and negative electrodes of the electrochemical cell, reactions occur at the working electrode (anode) and the counter electrode (cathode). Taking the example of a carbon monoxide sensor, the chemical reaction can be represented by the following equation:
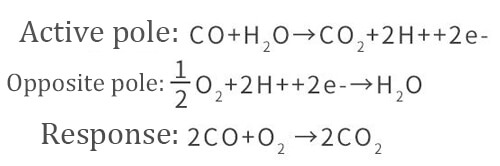
The oxidation-reduction reaction continuously occurs between the working electrode and the counter electrode, creating a potential difference between the electrodes. However, due to the polarization of the electrodes caused by the reactions occurring at both electrodes, it becomes challenging to maintain a constant potential between the electrodes. This limitation also affects the detectable range of carbon monoxide concentration.
The overall reaction involves the oxidation of carbon monoxide to carbon dioxide, resulting in the flow of electrons and the generation of an external current. Charge balance is achieved through the movement of charge carriers in the electrolyte.
The main characteristic of electrochemical sensors is that the current is directly proportional to the carbon monoxide concentration, and the output signal exhibits a good linear relationship with the gas concentration. This makes signal processing and displays conveniently. Another advantage is that these sensors operate at room temperature, eliminating the need for heaters. As a result, the electrode potential can be powered by dry batteries, eliminating the need for mains power.
Infrared sensors
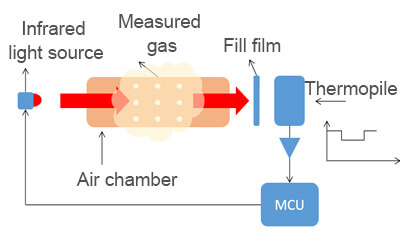
Pros: Wide measurement range, high accuracy, less susceptible to environmental interference.
Cons: High cost, higher maintenance requirements, larger size, lower accuracy in detecting low concentrations, not suitable for long-term power supply usage.
The detection principle of infrared sensors is as follows: Molecules composed of two different atoms have a dipole moment (product of the dipole length and the charge of one end of the dipole). When infrared light is irradiated onto a gas, it will absorb light of specific wavelengths that are related to the molecular structure of that gas.
The absorbed wavelengths can determine the type of gas, and the intensity of absorption can be used to measure the concentration of the gas. Infrared sensors have high sensitivity and accuracy, making them commonly used in instrumentation. However, they have a complex structure and higher cost, which limits their use in alarm systems.
Catalytic combustion sensors
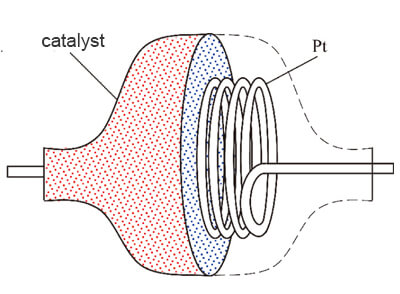
Pros: Accurate measurement, fast response time, long lifespan.
Cons: Operates in a flame state, posing a combustion and explosion hazard. Most elements are susceptible to poisoning by organic vapors.
Catalytic combustion sensors consist of a pair of sensing elements. One of the elements is highly sensitive to carbon monoxide gas and is coated with multiple layers of catalyst. The other element is insensitive and is used to compensate for changes in ambient temperature. This pair of sensing elements, along with another pair of high-precision resistors, forms a Wheatstone bridge.
Carbon monoxide detectors in four main areas
Carbon monoxide monitoring in mines
The concentration of carbon monoxide is an important indicator for monitoring the occurrence of fires in coal mines. Additionally, during drilling operations in transportation tunnels, coal mines can experience internal combustion, resulting in the release of large amounts of carbon monoxide and potentially causing carbon monoxide poisoning accidents. Portable carbon monoxide sensors are the optimal choice for mine workers as they are compact in size and can be carried by personnel. They allow for the monitoring of carbon monoxide concentrations at different locations.

Carbon monoxide monitoring in home
Malfunctions or aging of home heating systems, water heaters, and any other gas, oil, or coal-burning equipment can potentially lead to an increase in indoor carbon monoxide levels. Therefore, it is essential to install a carbon monoxide detector in your home and check or replace the batteries annually during the spring and fall time changes.

Home carbon monoxide detector is typically available in battery-powered or plug-in models. Battery-powered detectors can be installed at any location in the room, and you simply need to regularly check the battery status. Plug-in detectors can be inserted into wall outlets and may also have backup battery options to ensure continuous monitoring in case of power failure. Before choosing a home carbon monoxide detector, it is advisable to conduct some research and determine if there are any specific types or configurations required by local laws or regulations.
Carbon monoxide monitoring in parking lots
When vehicles remain running or idle in parking lots, a significant amount of carbon monoxide gas can be generated. If not properly ventilated, this can pose a safety risk. Therefore, it is necessary to establish a comprehensive carbon monoxide monitoring system in parking lots, utilizing carbon monoxide detectors installed at various enclosed points for 24/7 continuous monitoring.
Once the carbon monoxide detector in the parking lot detects an excessive level of carbon monoxide concentration, it will automatically activate ventilation devices. The ventilation system will remain active until the carbon monoxide concentration decreases to a safe level, at which point it will automatically shut off. All operations and monitoring data can be remotely accessed and viewed by professionals.
Wired installation of carbon monoxide sensor is the most reliable choice. Connecting the sensors to a controller via signal wires ensures more accurate automatic control functionality. The electrochemical working principle of the sensors provides more precise measurement results and helps avoid interference from other gases in the parking lot. Multiple carbon monoxide sensors can be installed at various locations in the parking lot, and the data can be monitored and managed centrally.
Carbon monoxide monitoring in industrial plants
Real-time monitoring of carbon monoxide levels in the environment and the concentration of carbon monoxide emissions from industrial exhaust is crucial in industrial production processes. It enables the timely detection and control of industrial emissions. The commonly used carbon monoxide detector in industrial environments is an explosion-proof carbon monoxide detector and duct-mounted carbon monoxide sensor.
An explosion-proof carbon monoxide detector is designed to monitor carbon monoxide concentration in potentially flammable or explosive environments. The stainless steel casing of these detectors ensures their reliable operation even in harsh conditions. For monitoring carbon monoxide concentration in enclosed pipelines, a duct mounted carbon monoxide sensor is the optimal choice.
Where to install carbon monoxide detector?
The carbon monoxide detector is categorized as residential and industrial. During cold winters, if coal is frequently used for heating, it is important to ensure proper ventilation by regularly opening windows to prevent the accumulation of carbon monoxide gas. It is recommended to install a carbon monoxide detector on every floor of your home, including the basement. The detectors should be placed within 10 feet of each bedroom door, and it is also advisable to install one in any garage. Each carbon monoxide detector should be inspected and replaced in a timely manner. When installing in your home, avoid placing detectors in the kitchen or close to cooking appliances. These areas can temporarily generate high concentrations of carbon monoxide, and installing detectors too close may result in frequent false alarms and noise.
In industrial settings, carbon monoxide sensors should be installed wherever significant amounts of carbon monoxide are likely to be generated. Examples include coal mines, non-ferrous metal mines, chemical fertilizer plants, steel mills, the machinery industry, organic chemical raw material manufacturing, and textile industry, among others. These industries are prone to the production of carbon monoxide due to chemical reactions, and installing carbon monoxide sensors is crucial to protect the safety of workers.
What do I do if my carbon monoxide detector goes off?
First, stay calm. Open all the doors and windows in your home to allow fresh air to circulate. Gather everyone in the house and go outside to breathe fresh air, avoiding prolonged exposure to carbon monoxide.
Next, check the health status of yourself and your family members. If anyone experiences any discomfort, promptly call 911.
Lastly, do not re-enter your home until the alarm stops or emergency responders deem it safe. Contact professionals to assess any other potential sources of carbon monoxide to prevent future incidents. Regularly maintain and inspect your home for any safety hazards, such as aging water heaters or cracks in the fireplace.